In commercial maintenance, various approaches are used to ensure the efficient operation of equipment. Among these, corrective, preventive, and predictive maintenance stand out. Understanding the differences between these strategies and Condition-Based Maintenance (CBM) is crucial to adopting more effective solutions tailored to supermarket needs, where refrigeration and air conditioning systems are critical.
Definition and Comparison of Maintenance Strategies
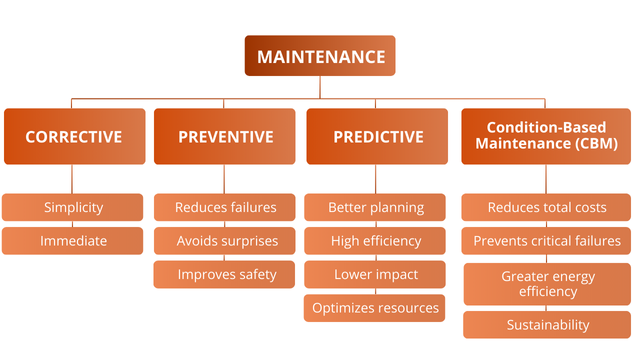
- Corrective Maintenance
- Definition: Also called reactive maintenance, it occurs after a failure has already happened. Widely used in food retail.
- Avantage : Simple and immediate, requiring little or no prevention.
- Disadvantage: Can lead to high costs due to operational downtime and wear on adjacent components. In supermarkets, it can result in loss of refrigerated products and customer discomfort.
- Preventive Maintenance
- Definition: Performed at scheduled intervals, based on equipment usage time or operation cycles. Increasingly applied in supermarkets in recent years.
- Avantage : Reduces the likelihood of unexpected failures.
- Disadvantage: Not always necessary, potentially generating additional costs for premature replacements.
- Predictive Maintenance
- Definition: Based on periodic measurements and analysis of equipment conditions to predict imminent failures. Rarely used in supermarkets.
- Avantage : Enables more efficient planning of interventions.
- Disadvantage: Requires specific technology and trained personnel to interpret the data.
- Condition-Based Maintenance (CBM)
- Definition: Continuously monitors equipment conditions using sensors and advanced technologies, allowing maintenance only when necessary.
- Avantage : Reduces costs of unnecessary interventions and prevents unexpected failures.
- Disadvantage: Requires an initial investment in sensors and monitoring infrastructure.
Exclusive Advantages of CBM
Condition-Based Maintenance stands out for its unique advantages, especially in applications involving critical systems such as refrigeration and air conditioning in supermarkets:
- Energy Efficiency: Continuous monitoring identifies inefficiencies, such as overloaded compressors or leaks in refrigeration systems, that increase energy consumption.
- Reduction in Operating Costs: By avoiding unexpected failures, CBM minimizes the need for emergency maintenance, which is typically more expensive.
- Extended Equipment Lifespan: CBM ensures equipment operates under optimal conditions, reducing premature wear.
- Proactive Planning: Enables interventions to be scheduled in ways that minimize impacts on supermarket operations.
Impacts on Energy Efficiency and Consumption Reduction
CBM has direct impacts on energy efficiency and consumption reduction in supermarkets. By identifying and correcting issues such as refrigerant leaks, motor overheating, or low efficiency in heat exchangers, CBM:
- Optimizes equipment performance: Systems tuned for optimal operation consume less energy.
- Reduces resource waste: Detects early failures that could lead to increased consumption.
- Promotes sustainability: More efficient equipment helps reduce carbon emissions and achieve environmental goals.
Conclusion
Each maintenance approach has specific applications, but CBM stands out as the most advanced option for refrigeration and air conditioning systems in supermarkets. By continuously monitoring operational conditions, it offers a unique combination of efficiency, predictability, and cost reduction.
Ready to optimize your supermarket’s maintenance? Click here and Discover how NEO Estech and CBM can transform your operations and deliver sustainable results!