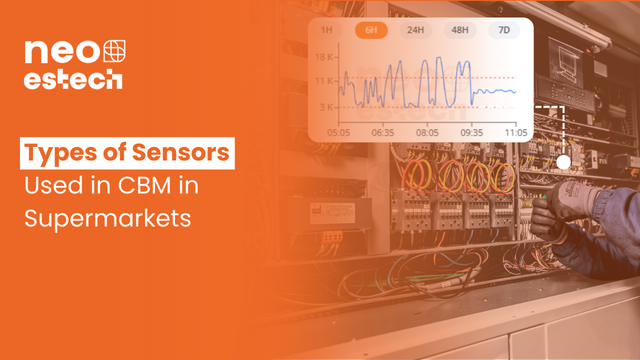
The use of sensors in refrigeration, air conditioning, and energy systems has revolutionized maintenance in supermarkets. In the context of Condition-Based Maintenance (CBM), sensors play an essential role in continuous monitoring, failure prevention, and energy efficiency improvement. This article explores the main types of sensors, how to choose them, and their direct impacts on operation.
Sensor Classification by Application
- 1. Temperature Sensors:
- Used to monitor temperatures in cold rooms, frozen islands, and air conditioning systems. Detect overheating or variations that may compromise product quality.
- They detect overheating or variations that may compromise the quality of the products.
- 2. Pressure Sensors:
- Monitor the performance of compressors and heat exchangers.
- Ensure the system operates within ideal limits, preventing failures.
- Flow Sensors:
- Evaluate the operation of electronic expansion valves, in addition to monitoring the modulation of compressors and condensers to ensure efficient operations.
- Energy Sensors:
- Measure the electrical consumption of critical components.
- Identify equipment with low performance or excessive consumption.
- Operation Confirmation Sensors:
- Indicated to verify if the equipment is effectively in operation.
- Indicated to verify if equipment is effectively in operation. Essential to monitor motors, compressors, and fans, ensuring they are operating as expected.
- Gateways:
- Devices that communicate with existing automation systems.
- Extract valuable data from components such as frequency inverters, allowing for a more detailed analysis of system performance.
Criteria for Choosing Efficient Sensors
- Compatibility:
- Ensure the sensor is compatible with the existing automation and monitoring system.
- Accuracy and Reliability:
- Choose sensors that offer precise measurements and are designed to operate in environments with humidity and low temperature.
- Cost-Benefit:
- Evaluate the return on investment based on the reduction of operational costs and the increase in equipment lifespan.
- Simplified Maintenance:
- Prefer sensors that are easy to install, calibrate, and replace, minimizing downtime, for example, by replacing a low-lifespan battery.
- Integration with IoT:
- Opt for sensors that can be connected to cloud-based platforms for remote monitoring.
- Communication Network:
- Evaluate the best option between wired and wireless to connect sensors and gateways. Wired networks offer greater reliability and resistance to interference, but may have higher installation costs and less flexibility. Wireless networks are ideal for dynamic installations or hard-to-reach locations, but may suffer interference in environments with a large presence of metals or competing signals. Also consider the maintenance and durability of each type when planning the communication infrastructure.
Reducing Downtime with Sensors
Sensors allow identifying anomalies before serious failures occur, significantly reducing the downtime of refrigeration and air conditioning systems. For example:
- 3. Vibration Sensors: Alert about mechanical imbalances, enabling the preventive replacement of worn components.
- 2. Pressure Sensors: Detect fluctuations that indicate problems in compressors, allowing for scheduled interventions.
In addition, with operation confirmation sensors, it is possible to ensure that the equipment is operating at the expected time, avoiding operational losses.
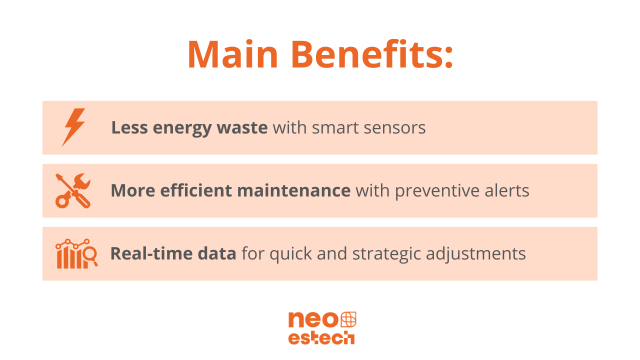
Reducing Energy Consumption with Smart Sensors
The integration of smart sensors into CBM systems results in a significant reduction in energy consumption:
- Equipment Optimization:
- Energy sensors identify inefficient components and guide adjustments to minimize waste.
- Overload Prevention:
- Temperature and pressure sensors ensure that systems operate in ideal conditions, avoiding excessive consumption.
- 1. Continuous Monitoring:
- Real-time data allows for quick adjustments, increasing operational efficiency.
- Integration with Gateways:
- Gateways allow extracting data directly from existing controllers, offering insights into performance and automatically adjusting operations for greater efficiency.
Conclusion
The correct selection of sensors for CBM in supermarkets is fundamental to ensure energy efficiency, reduce costs, and avoid unplanned shutdowns. These devices, combined with a robust maintenance strategy, transform the way assets are managed, providing greater reliability and sustainability.
Ready to elevate your maintenance management with smart sensors? Discover how we can help optimize your systems and maximize results!